
When we consider the vast and fascinating realm of space exploration, one name that invariably comes to mind is **Neil Armstrong**. He is far more than just a name; he represents the pinnacle of human achievement and the relentless pursuit of knowledge beyond our planet. As the first individual to ever set foot on the Moon, Armstrong’s journey is a testament to courage, innovation, and the spirit of exploration. His historic lunar landing on July 20, 1969, during NASA’s Apollo 11 mission, marked a monumental milestone in human history. It was a moment that captivated the world and inspired generations to dream big. In this exploration of his life, we will delve into the experiences and challenges that shaped Armstrong into the iconic astronaut he became, examining the pivotal moments that led him to play such a crucial role in the annals of space exploration. From his early years to his groundbreaking achievements, Armstrong’s story is one of determination, skill, and an unwavering commitment to pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
Early Life: The Seeds of Passion

Childhood in Wapakoneta, Ohio
Neil Armstrong was born on August 5, 1930, in the small town of Wapakoneta, Ohio, where he would spend his formative years. As the eldest of three children in the Armstrong family, he was raised by his parents, Viola Louise Engel and Stephen Koenig Armstrong, who played a pivotal role in shaping his character. They nurtured his natural curiosity and encouraged a spirit of adventure that would define his life. At the tender age of six, Neil experienced his first airplane ride, an exhilarating moment that sparked a profound and enduring passion for aviation that would follow him throughout his life.
Becoming a Pilot
Imagine the thrill of becoming a licensed pilot at just 16 years old! Neil Armstrong reached this remarkable milestone on his own birthday, a testament to his unwavering determination and deep love for flying. Shortly after obtaining his pilot’s license, he joined the naval air cadet program, marking the beginning of a promising career in aviation. This early achievement not only showcased his exceptional skills but also set the foundation for his future endeavors, ultimately leading him to become one of the most celebrated astronauts in history.
Education and Early Career
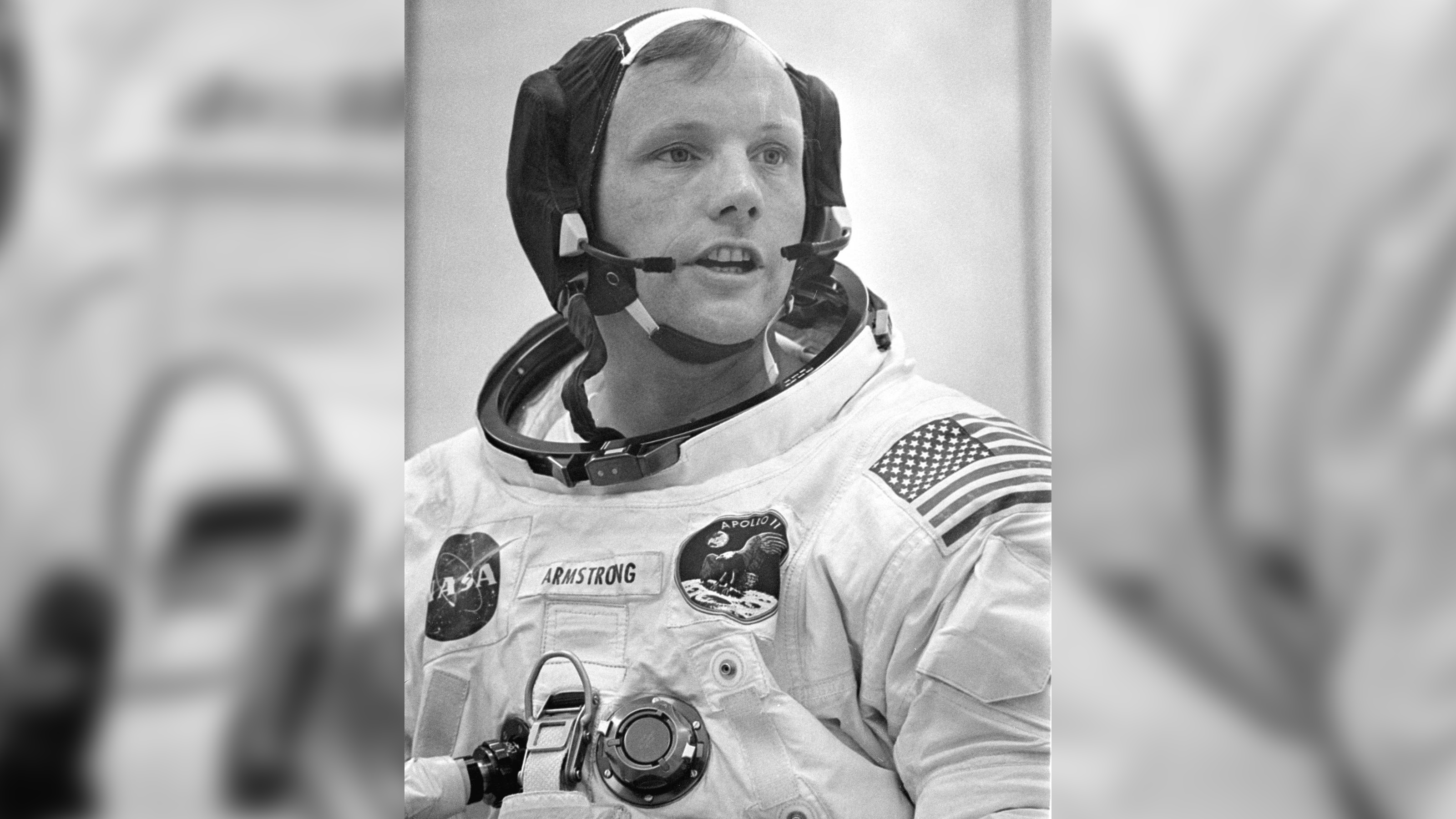

Purdue University and Military Service
Neil Armstrong began his academic journey at Purdue University, where he dedicated himself to the rigorous study of aeronautical engineering. His passion for aviation and engineering was evident, but his educational pursuits faced an unexpected interruption due to the outbreak of the Korean War. During this tumultuous period, Armstrong served his country as a naval aviator, a role that would significantly shape his future. His time in the military was marked by remarkable bravery; he was shot down during a mission, an experience that tested his resilience and courage. For his exceptional service and valor in the face of danger, he was awarded three prestigious Air Medals, recognizing his contributions and heroism in combat.
Research Pilot at NASA
Upon completing his degree in 1955, Armstrong transitioned into a groundbreaking career by joining the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), which would later evolve into the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). In this role, he became a highly skilled research pilot, accumulating over 2,450 hours of flight time across a diverse array of aircraft. This extensive experience not only refined his piloting abilities but also deepened his understanding of aeronautical science, preparing him for the monumental challenges that lay ahead in the realm of space exploration.
Joining the Space Program

The Second Group of Astronauts
In the year 1962, a significant milestone in Neil Armstrong’s career occurred when he was selected as a member of NASA’s second group of astronauts. This selection was not just a personal achievement for Armstrong; it marked the beginning of an extraordinary journey that would ultimately have a profound impact on the world. As he prepared to enter the realm of space exploration, Armstrong was filled with a sense of purpose and determination, knowing that he was about to contribute to one of humanity’s most ambitious endeavors—venturing beyond our planet and into the vast unknown of outer space.
Gemini 8 Mission
On March 16, 1966, Armstrong took command of the historic Gemini 8 mission, a pivotal moment in the annals of space exploration. During this mission, he achieved a remarkable feat by successfully executing the first manual docking of two spacecraft in orbit. This accomplishment was a testament to his exceptional skills and training. However, the mission took an unexpected turn when a malfunction caused the spacecraft to spin uncontrollably, putting both Armstrong and his co-pilot in a precarious situation. Demonstrating remarkable composure and quick thinking, Armstrong skillfully regained control of the spacecraft, averting a potential disaster. His ability to remain calm under pressure not only saved the mission but also highlighted his extraordinary capabilities as an astronaut and leader in the face of adversity.
The Historic Apollo 11 Mission

Blast Off to the Moon
Fast forward to July 16, 1969. Armstrong, along with Buzz Aldrin and Michael Collins, launched aboard the Apollo 11 spacecraft. This mission was not just about reaching the Moon; it was about making history.
The Moon Landing
On July 20, 1969, the world held its breath as the Eagle lunar module touched down on the Moon. At 10:56 PM EDT, Armstrong stepped onto the lunar surface, uttering the iconic words, “That’s one small step for [a] man, one giant leap for mankind.” Can you feel the weight of that moment?
Scientific Contributions on the Moon
During their time on the Moon, Armstrong and Aldrin conducted over 21 hours of scientific tests, collected samples, and took numerous photographs. Their work laid the groundwork for future lunar exploration.
Life After Apollo 11

Global Recognition
After the success of Apollo 11, Armstrong and his crewmates embarked on a world tour, visiting over 20 countries to celebrate their achievement. Armstrong received the Presidential Medal of Freedom in 1969, a testament to his contributions to humanity.
Academic Pursuits
In 1971, Armstrong resigned from NASA and became a professor of aerospace engineering at the University of Cincinnati. He preferred to stay out of the limelight, focusing on education and mentoring the next generation of engineers.
Legacy and Honors
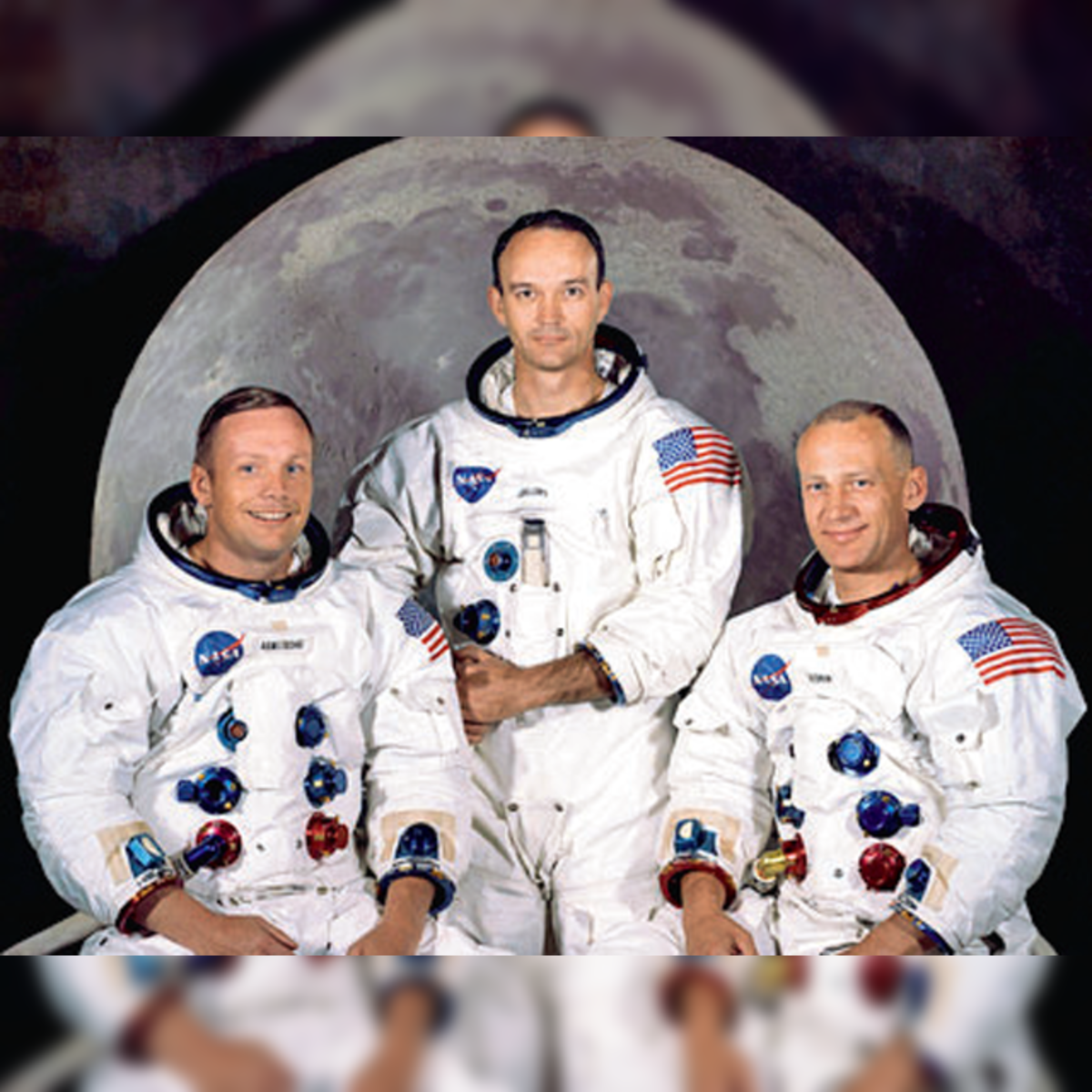

A Lasting Impact on Space Exploration
Neil Armstrong’s legacy extends beyond his Moon landing. He served on various boards and commissions, including the Presidential Commission on the Space Shuttle Challenger Accident. His insights and expertise helped shape the future of space exploration.
Awards and Recognition
Throughout his life, Armstrong received numerous accolades, including the Congressional Space Medal of Honor in 1978 and the Congressional Gold Medal in 2009. These honors reflect his significant contributions to science and exploration.
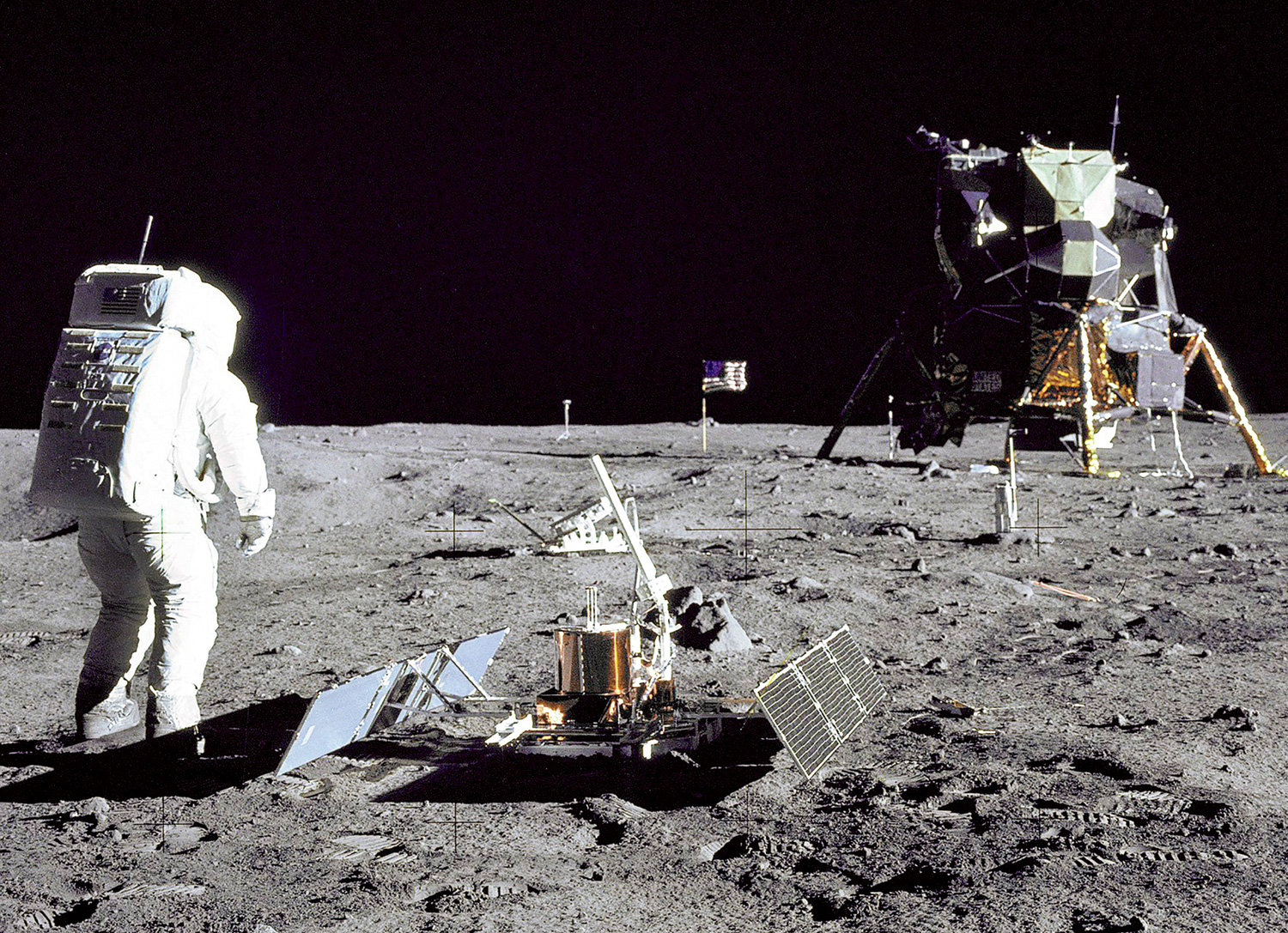
Neil Armstrong passed away on August 25, 2012, but his spirit lives on. He was more than just an astronaut; he was a pioneer who dared to dream big. His journey from a small town in Ohio to the Moon is a reminder that with passion and perseverance, anything is possible. So, the next time you look up at the night sky, remember the man who took that giant leap for mankind.
Timeline of Apollo Missions

| Mission | Date | Key Achievement |
|---|---|---|
| Apollo 1 | January 27, 1967 | Tragic fire during a pre-launch test |
| Apollo 7 | October 11, 1968 | First successful crewed Apollo mission |
| Apollo 11 | July 16, 1969 | First Moon landing |
| Apollo 12 | November 14, 1969 | Second Moon landing |
| Apollo 13 | April 11, 1970 | Successful failure; crew returned safely |
| Apollo 17 | December 7, 1972 | Last crewed Moon landing |

